Building clusters
In the
input/omnia_config.yml,input/security_config.yml,input/telemetry_config.ymland [optional]input/storage_config.ymlfiles, provide the required details.
Note
Use the parameter
scheduler_typeininput/omnia_config.ymlto customize what schedulers are installed in the cluster.Without the login node, Slurm jobs can be scheduled only through the manager node.
Create an inventory file in the omnia folder. Check out the sample inventory for more information.
[Manager] group should contain the manager node IP address. [1]
[compute] group should contain all compute node IP addresses.
[login] group should contain the login node IP.
- Hostname requirements
The Hostname should not contain the following characters: , (comma), . (period) or _ (underscore). However, the domain name is allowed commas and periods.
The Hostname cannot start or end with a hyphen (-).
No upper case characters are allowed in the hostname.
The hostname cannot start with a number.
The hostname and the domain name (that is:
hostname00000x.domain.xxx) cumulatively cannot exceed 64 characters. For example, if thenode_nameprovided ininput/provision_config.ymlis ‘node’, and thedomain_nameprovided is ‘omnia.test’, Omnia will set the hostname of a target cluster node to ‘node00001.omnia.test’. Omnia appends 6 digits to the hostname to individually name each target node.
Note
RedHat nodes that are not configured by Omnia need to have a valid subscription. To set up a subscription, click here.
Omnia creates a log file which is available at:
/var/log/omnia.log.If only Slurm is being installed on the cluster, docker credentials are not required.
omnia.ymlis a wrapper playbook comprising of:security.yml: This playbook sets up centralized authentication (LDAP/FreeIPA) on the cluster. For more information, click here.scheduler.yml: This playbook sets up job schedulers (Slurm or Kubernetes) on the cluster.storage.yml: This playbook sets up storage tools like BeeGFS and NFS.telemetry.yml: This playbook sets up Omnia telemetry and/or iDRAC telemetry. It also installs Grafana and Loki as Kubernetes pods.
To run omnia.yml:
ansible-playbook omnia.yml -i inventory
Note
To visualize the cluster (Slurm/Kubernetes) metrics on Grafana (On the control plane) during the run of
omnia.yml, add the parametersgrafana_usernameandgrafana_password(That isansible-playbook omnia.yml -i inventory -e grafana_username="" -e grafana_password="").Having the same node in the manager and login groups in the inventory is not recommended by Omnia.
If you want to view or edit the
omnia_config.ymlfile, run the following command:ansible-vault view omnia_config.yml --vault-password-file .omnia_vault_key– To view the file.ansible-vault edit omnia_config.yml --vault-password-file .omnia_vault_key– To edit the file.
Use the ansible-vault view or edit commands and not the ansible-vault decrypt or encrypt commands. If you have used the ansible-vault decrypt or encrypt commands, provide 644 permission to the parameter files.
Setting up a shared home directory
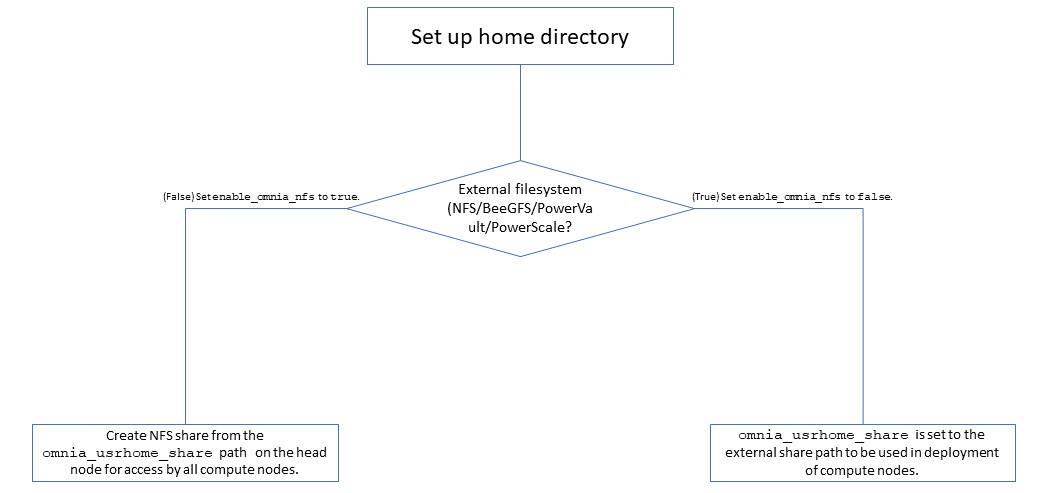
Users wanting to set up a shared home directory for the cluster can do it in one of two ways:
Using the head node as an NFS host: Set
enable_omnia_nfs(input/omnia_config.yml) to true and provide a share path which will be configured on all nodes inomnia_usrhome_share(input/omnia_config.yml). During the execution ofomnia.yml, the NFS share will be set up for access by all cluster nodes.Using an external filesystem: Configure the external file storage using
storage.yml. Setenable_omnia_nfs(input/omnia_config.yml) to false and provide the external share path inomnia_usrhome_share(input/omnia_config.yml). Runomnia.ymlto configure access to the external share for deployments.
Slurm job based user access
To ensure security while running jobs on the cluster, users can be assigned permissions to access cluster nodes only while their jobs are running. To enable the feature:
cd scheduler
ansible-playbook job_based_user_access.yml -i inventory
Note
The inventory queried in the above command is to be created by the user prior to running
omnia.ymlasscheduler.ymlis invoked byomnia.ymlOnly users added to the ‘slurm’ group can execute slurm jobs. To add users to the group, use the command:
usermod -a -G slurm <username>.
Running Slurm MPI jobs on clusters
To enhance the productivity of the cluster, Slurm allows users to run jobs in a parallel-computing architecture. This is used to efficiently utilize all available computing resources. Click here for more information.
Note
Omnia does not install MPI packages by default. Users hoping to leverage the Slurm-based MPI execution feature are required to install the relevant packages from a source of their choosing. For information on setting up Intel OneAPI on the cluster, click here.
Ensure there is an NFS node on which to host slurm scripts to run.
Running jobs as individual users (and not as root) requires that passwordSSH be enabled between cluster nodes for the user.
If you have any feedback about Omnia documentation, please reach out at omnia.readme@dell.com.