Product and Subsystem Security
Security controls map
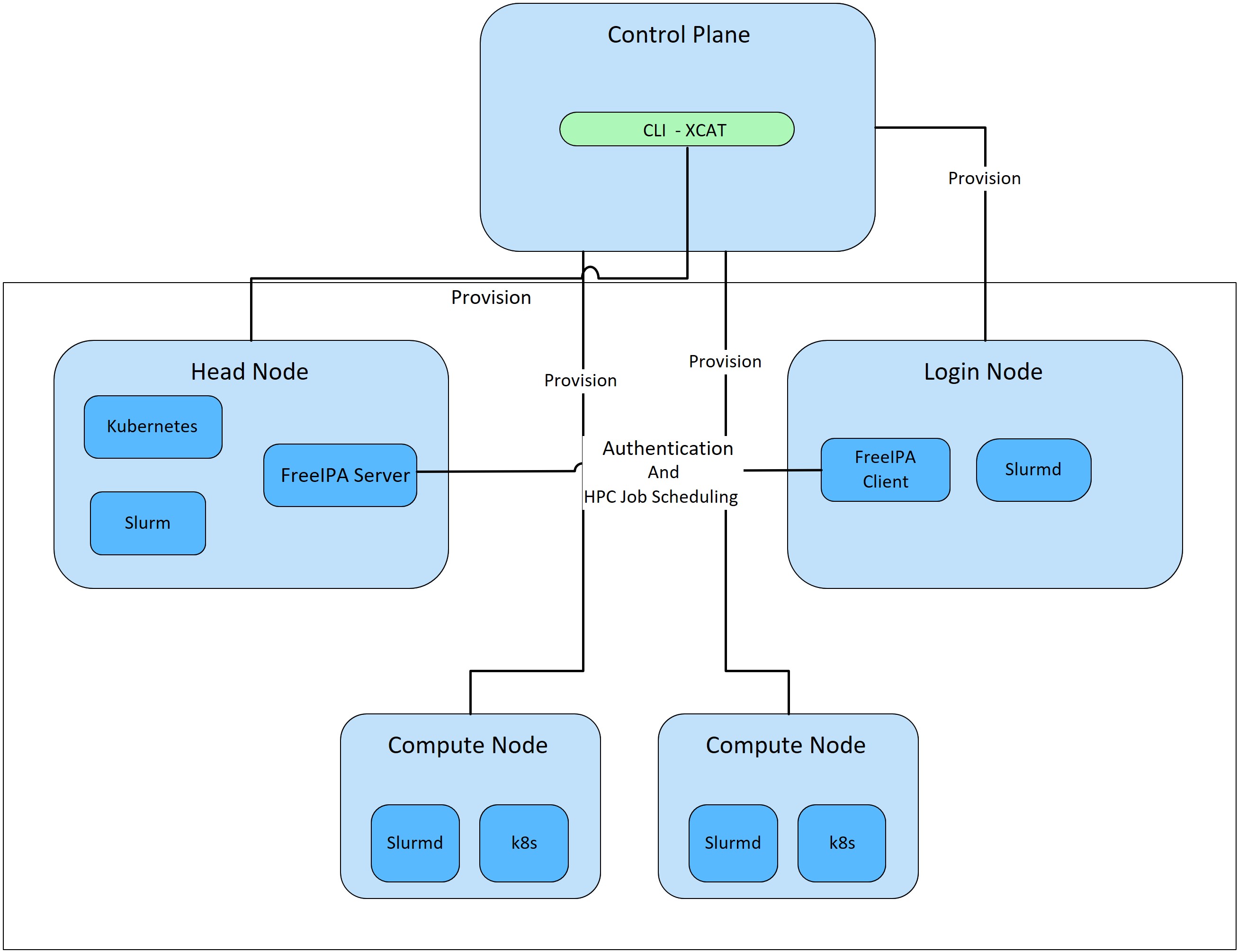
Omnia performs bare metal configuration to enable AI/HPC workloads. It uses Ansible playbooks to perform installations and configurations. iDRAC is supported for provisioning bare metal servers. Omnia installs xCAT to enable provisioning of clusters via PXE in different ways:
Mapping file [optional]: To dictate IP address/MAC mapping, a host mapping file can be provided.
BMC discovery [optional]: To discover the cluster via BMC (iDRAC), IPMI must be enabled on remote servers. Discovery happens over IPMI. For security best practices when using this method, click here!
Switch [default]: To discovery the cluster by routing communication through particular switch ports over SNMPv3, non-admin switch credentials must be provided.
Note
IPMI is not required on the control plane. However, compute nodes (iDRACs in the cluster/private network) require IPMI to be enabled for BMC discovery.
Omnia can be installed via CLI only. Slurm and Kubernetes are deployed and configured on the cluster. FreeIPA or LDAP is installed for providing authentication.
To perform these configurations and installations, a secure SSH channel is established between the management node and the following entities:
kube_control_plane
Compute Nodes
Login Node
Authentication
Omnia does not have its own authentication mechanism because bare metal installations and configurations take place using root privileges. Post the execution of Omnia, third-party tools are responsible for authentication to the respective tool.
Cluster authentication tool
In order to enable authentication to the cluster, Omnia installs FreeIPA: an open source tool providing integrated identity and authentication for Linux/UNIX networked environments. As part of the HPC cluster, the login node is responsible for configuring users and managing a limited number of administrative tasks. Access to the manager/head node is restricted to administrators with the root password. For authentication on the manager and compute nodes exclusively, LDAP can also be installed by Omnia on the client.
Note
Omnia does not configure LDAP users or groups.
Authentication types and setup
Key-Based authentication
Use of SSH authorized_keys
A password-less channel is created between the management station and compute nodes using SSH authorized keys. This is explained in the Security Controls Map.
Login security settings
The following credentials have to be entered to enable different tools on the management station:
iDRAC (Username/ Password)
Ethernet Switch (Username/ Password)
Infiniband Switch (Username/ Password)
PowerVault ME4/ME5 (Username/ Password)
Provisioning OS (Password)
SNMPv3 PXE switch (Non-admin username/ password)
Similarly, passwords for the following tools have to be provided in input/omnia_config.yml and input/provision_config_credentials.yml to configure the cluster:
maria_db (Password)
DockerHub (Username/ Password)
For setting up authentication on the cluster, the following credentials have to be provided in input/security_config.yml:
FreeIPA (directory_manager_password, ipa_admin_password)
LDAP (ldap_bind_username, ldap_bind_password)
Once Omnia is invoked, these files are validated and encrypted using Ansible Vault. They are hidden from external visibility and access.
Authentication to external systems
Third party software installed by Omnia are responsible for supporting and maintaining manufactured-unique or installation-unique secrets.
Configuring remote connections
When setting up BeeGFS client services on the cluster, a connection authentication file is used to maintain the security of the communications between server and client.
Generate the connection authentication file (connAuth) and use it to set up BeeGFS meta, server and storage services.
Copy the connAuth file to the control plane and note the filepath.
Populate the value of
beegfs_secret_storage_filepathininput/storage_config.ymlwith the filepath from the previous step.
Omnia will configure the BeeGFS clients on th cluster using the provided file. BeeGFS is responsible for maintaining and securing connAuthFile. For more information, click here.
Network security
Omnia configures the firewall as required by the third-party tools to enhance security by restricting inbound and outbound traffic to the TCP and UDP ports.
Network exposure
Omnia uses port 22 for SSH connections, same as Ansible.
Firewall settings
Omnia configures the following ports for use by third-party tools installed by Omnia.
Kubernetes ports requirements
Port
Number
Layer 4
Protocol Purpose Type of Node
6443
TCP
Kubernetes API
server Manager
2379-2380
TCP
etcd server
client API Manager
10251
TCP
Kube-scheduler Manager
10252
TCP
Kube-controller manager
Manager
10250
TCP
Kubelet API
Compute
30000-32767
TCP
Nodeport services
Compute
5473
TCP
Calico services
Manager/Compute
179
TCP
Calico services
Manager/Compute
4789
UDP
Calico services
Manager/Compute
8285
UDP
Flannel services
Manager/Compute
8472
UDP
Flannel services
Manager/Compute
Slurm port requirements
Port
Number
Layer 4
Protocol Node
6817
TCP/UDP
Slurmctld Port
Manager
6818
TCP/UDP
Slurmd Port
Compute
6819
TCP/UDP
Slurmdbd Port
Manager
BeeGFS port requirements
Port
Service
8008
Management service (beegfs-mgmtd)
8003
Storage service (beegfs-storage)
8004
Client service (beegfs-client)
8005
Metadata service (beegfs-meta)
8006
Helper service (beegfs-helperd)
xCAT port requirements
Port number
Protocol
Service Name
3001
tcp
xcatdport
3001
udp
xcatdport
3002
tcp
xcatiport
3002
udp
xcatiport
3003(default)
tcp
xcatlport
7
udp
echo-udp
22
tcp
ssh-tcp
22
udp
ssh-udp
873
tcp
rsync
873
udp
rsync
53
tcp
domain-tcp
53
udp
domain-udp
67
udp
bootps
67
tcp
dhcp
68
tcp
dhcpc
68
udp
bootpc
69
tcp
tftp-tcp
69
udp
tftp-udp
80
tcp
www-tcp
80
udp
www-udp
88
tcp
kerberos
88
udp
kerberos
111
udp
sunrpc-udp
443
udp
HTTPS
443
tcp
HTTPS
514
tcp
shell
514
tcp
rsyslogd
514
udp
rsyslogd
544
tcp
kshell
657
tcp
rmc-tcp
657
udp
rmc-udp
782
tcp
conserver
1058
tcp
nim
2049
tcp
nfsd-tcp
2049
udp
nfsd-udp
4011
tcp
pxe
300
tcp
awk
623
tcp
ipmi
623
udp
ipmi
161
tcp
snmp
161
udp
snmp
162
tcp
snmptrap
162
udp
snmptrap
5432
tcp
postgresDB
Note
For more information, check out the xCAT website.
FreeIPA port requirements
Port Number
Layer 4
Purpose
Node
80
TCP
HTTP/HTTPS
Manager/ Login_Node
443
TCP
HTTP/HTTPS
Manager/ Login_Node
389
TCP
LDAP/LDAPS
Manager/ Login_Node
636
TCP
LDAP/LDAPS
Manager/ Login_Node
88
TCP/UDP
Kerberos
Manager/ Login_Node
464
TCP/UDP
Kerberos
Manager/ Login_Node
53
TCP/UDP
DNS
Manager/ Login_Node
7389
TCP
Dogtag’s LDAP server
Manager/ Login_Node
123
UDP
NTP
Manager/ Login_Node
Note
To avoid security vulnerabilities, protocols can be restricted on the network using the parameters restrict_program_support and restrict_softwares in input/login_node_security_config.yml. However, certain protocols are essential to Omnia’s functioning and cannot be disabled. These protocols are: ftp, smbd, nmbd, automount, portmap.
Data security
Omnia does not store data. The passwords Omnia accepts as input to configure the third party tools are validated and then encrypted using Ansible Vault. Run yum update --security routinely on the control plane for the latest security updates.
For more information on the passwords used by Omnia, see Login Security Settings.
Auditing and logging
Omnia creates a log file at /var/log/omnia on the management station. The events during the installation of Omnia are captured as logs. For different roles called by Omnia, separate log files are created as listed below:
monitor.log
network.log
provision.log
scheduler.log
security.log
storage.log
utils.log
Additionally, an aggregate of the events taking place during storage, scheduler and network role installation called omnia.log is created in /var/log.
There are separate logs generated by the third party tools installed by Omnia.
Logs
A sample of the omnia.log is provided below:
2021-02-15 15:17:36,877 p=2778 u=omnia n=ansible | [WARNING]: provided hosts
list is empty, only localhost is available. Note that the implicit localhost does not
match 'all'
2021-02-15 15:17:37,396 p=2778 u=omnia n=ansible | PLAY [Executing omnia roles]
************************************************************************************
2021-02-15 15:17:37,454 p=2778 u=omnia n=ansible | TASK [Gathering Facts]
*****************************************************************************************
*
2021-02-15 15:17:38,856 p=2778 u=omnia n=ansible | ok: [localhost]
2021-02-15 15:17:38,885 p=2778 u=omnia n=ansible | TASK [common : Mount Path]
**************************************************************************************
2021-02-15 15:17:38,969 p=2778 u=omnia n=ansible | ok: [localhost]
These logs are intended to enable debugging.
Note
The Omnia product recommends that product users apply masking rules on personal identifiable information (PII) in the logs before sending to external monitoring applications or sources.
Logging format
Every log message begins with a timestamp and also carries information on the invoking play and task.
The format is described in the following table.
Field |
Format |
Sample Value |
|---|---|---|
Timestamp |
yyyy-mm-dd h:m:s |
2/15/2021 15:17 |
Process Id |
p=xxxx |
p=2778 |
User |
u=xxxx |
u=omnia |
Name of the process executing |
n=xxxx |
n=ansible |
The task being executed/ invoked |
PLAY/TASK |
[Gathering Facts] |
Error |
fatal: [hostname]: Error Message |
“lookup_plugin.lines} |
Warning |
[WARNING]: warning message |
[WARNING]: provided hosts list is empty |
Network vulnerability scanning
Omnia performs network security scans on all modules of the product. Omnia additionally performs Blackduck scans on the open source softwares, which are installed by Omnia at runtime. However, Omnia is not responsible for the third-party software installed using Omnia. Review all third party software before using Omnia to install it.
If you have any feedback about Omnia documentation, please reach out at omnia.readme@dell.com.